Performace analysis
how to find the bottleneck of the server performace.
Check out this fabulous pic from http://www.brendangregg.com/linuxperf.html
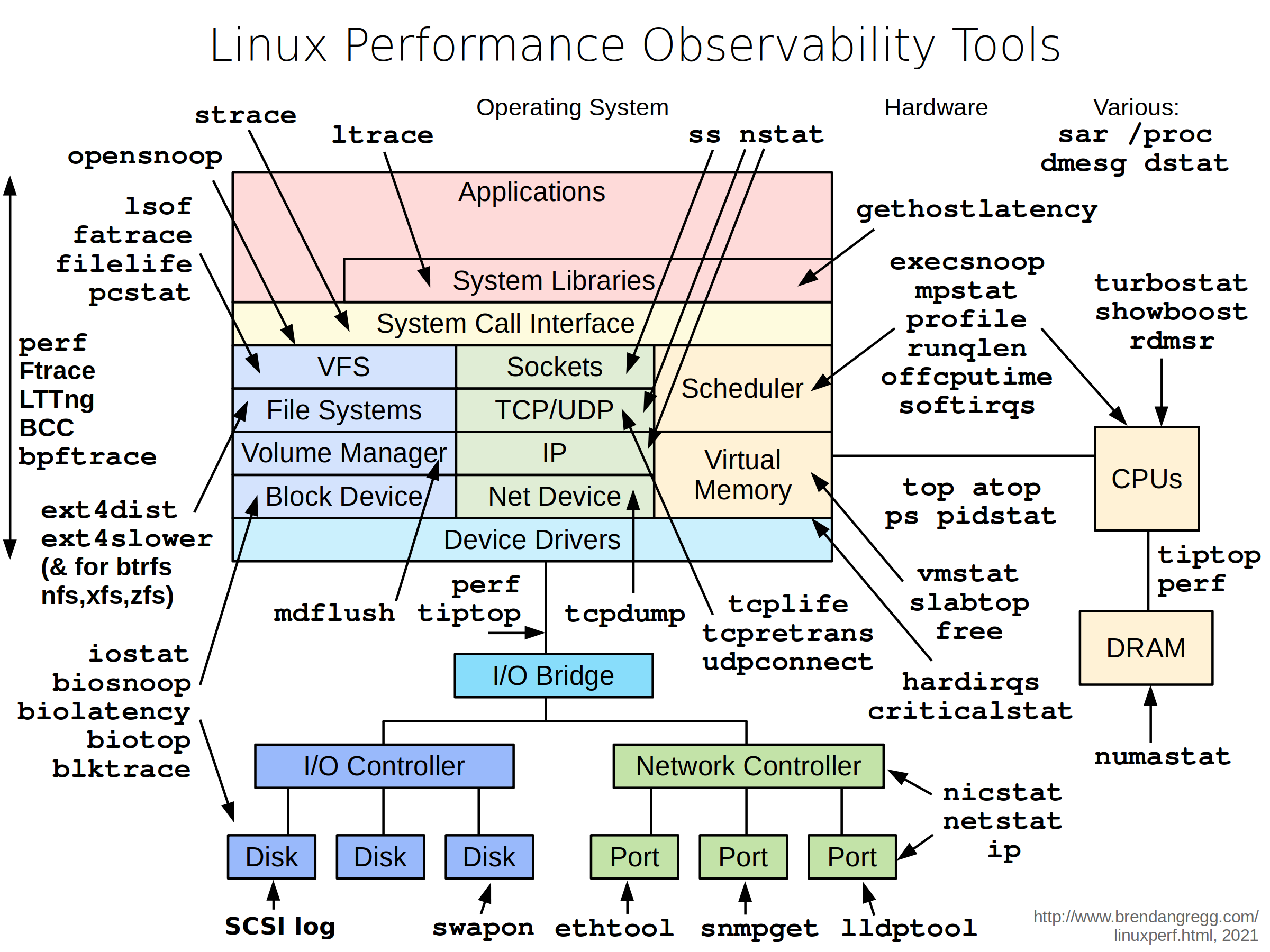
and this great slices: http://www.slideshare.net/brendangregg/linux-performance-tools
First you need to monitor you server and services, you can use munin, there are a lot of options.
When the service slow down, I would login to the service, using the following tools:
-
htop
htop is great, it's like
top, but better, I highly recommend this tool.
watch the
load, ifload> number of CPUs, may mean CPU saturation -
vmstat
$ vmstat 1 procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- ... r b swpd free buff cache si so ... 9 0 0 29549320 29252 9299060 0 ... 2 0 0 29547876 29252 9299332 0 ... 4 0 0 29548124 29252 9299460 0 ... 5 0 0 29548840 29252 9299592 0 ...
The procs data reports the number of processing jobs waiting to run and allows you to determine if there are processes “blocking” your system from running smoothly.
The
rcolumn displays the total number of processes waiting for access to the processor. Thebcolumn displays the total number of processes in a “sleep” state.I usually see
rvalue, if it's big, it means the server is in a high load.For other data meaning, ref: https://www.linode.com/docs/uptime/monitoring/use-vmstat-to-monitor-system-performance
-
iostat iotop
Block I/O status
$ iostat -xmdz 1
1st output is since boot. For more information refer 24 iostat, vmstat and mpstat Examples for Linux Performance Monitoring
iotop can show which process use most I/O.

-
pidstat
Very useful process stats. eg, by-thread, disk I/O:
-
iftop
iftop show the network usage with other hosts.

Nginx tunning
nginx.conf
keepalive_timeout: assigns the timeout for keep-alive connections with the client. Simply put, Nginx will close connections with the client after this period of time.
keep this small value, like keepalive_timeout 15;
Linux TCP Performance Tuning(sysctl.conf)
- /proc/sys/fs/file-max: The maximum number of concurrently open files.
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog: Maximum number of remembered connection requests, which are still did not receive an acknowledgment from connecting client. The default value is 1024 for systems with more than 128Mb of memory, and 128 for low memory machines. If server suffers of overload, try to increase this number.
- /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn: Limit of socket listen() backlog, known in userspace as SOMAXCONN. Defaults to 128. The value should be raised substantially to support bursts of request. For example, to support a burst of 1024 requests, set somaxconn to 1024.
There are two ways to change tcp parameters.
-
change the value of parameter files in /proc/sys/net/ e.g. increase the value of somaxconn
echo 1024 > /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconnwhen the server restart, the parameter will restore. -
change the vlaue in /etc/sysctl.con, and run
sudo sysctl -pto apply the changes immediately, this can change the value permanently.